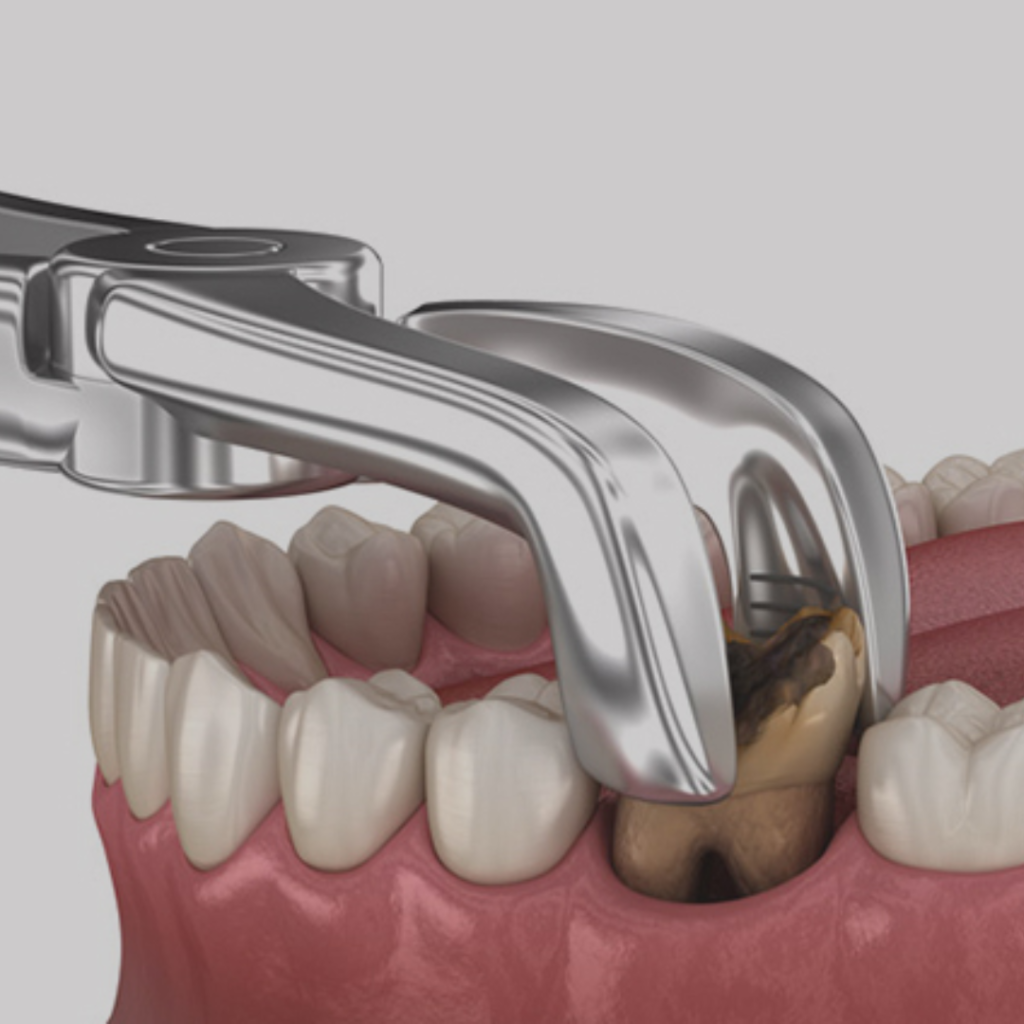
Oral Surgery
Oral surgery refers to any surgical procedure performed on your teeth, gums, jaws or other oral structures. This includes extractions, implants, gum grafts and jaw surgeries. Oral surgery is usually performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon or a periodontist. These are dental specialists who have advanced training in oral surgery procedures.
What is oral surgery?
Oral surgery is a broad term for any operation performed on your teeth, gums, jaw or surrounding oral and facial structures. It includes a wide range of procedures, including teeth extractions, dental bone grafts, periodontal (gum) grafts and corrective jaw surgery.
Why is oral surgery performed?
Why is oral surgery performed?
You could need oral surgery for a number of reasons. Your dentist might recommend it if you have:
- Extensive tooth decay.
- Badly broken teeth.
- Gum disease.
- Impacted teeth.
- Missing teeth.
- Temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD).
- Bone loss in your jaw.
- Sleep apnea.
- Oral cancer.
- Benign oral pathology (noncancerous lumps or bumps).
What happens during oral surgery?
Sometimes, oral surgery is performed in a dental office as an outpatient procedure. Your surgeon may offer sedation options for your comfort, including nitrous oxide, oral medications or intravenous (IV) moderate or deep sedation. In other cases, oral surgery may be completed in a hospital under general anesthesia.
What happens after oral surgery?
Following your oral surgery procedure, you’ll be given detailed post-operative instructions. It’s important that you follow these guidelines closely to reduce your risk of bleeding, infection and other complications.
